 Space
Space
Articles under the Space category.
Rubin’s first images to first alerts: the real-time sky begins
With first images unveiled in June 2025, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory has entered commissioning toward nightly, petabyte-scale scans. Over the next year, real-time alerts will change what gets discovered, by whom, and how fast astronomy responds.
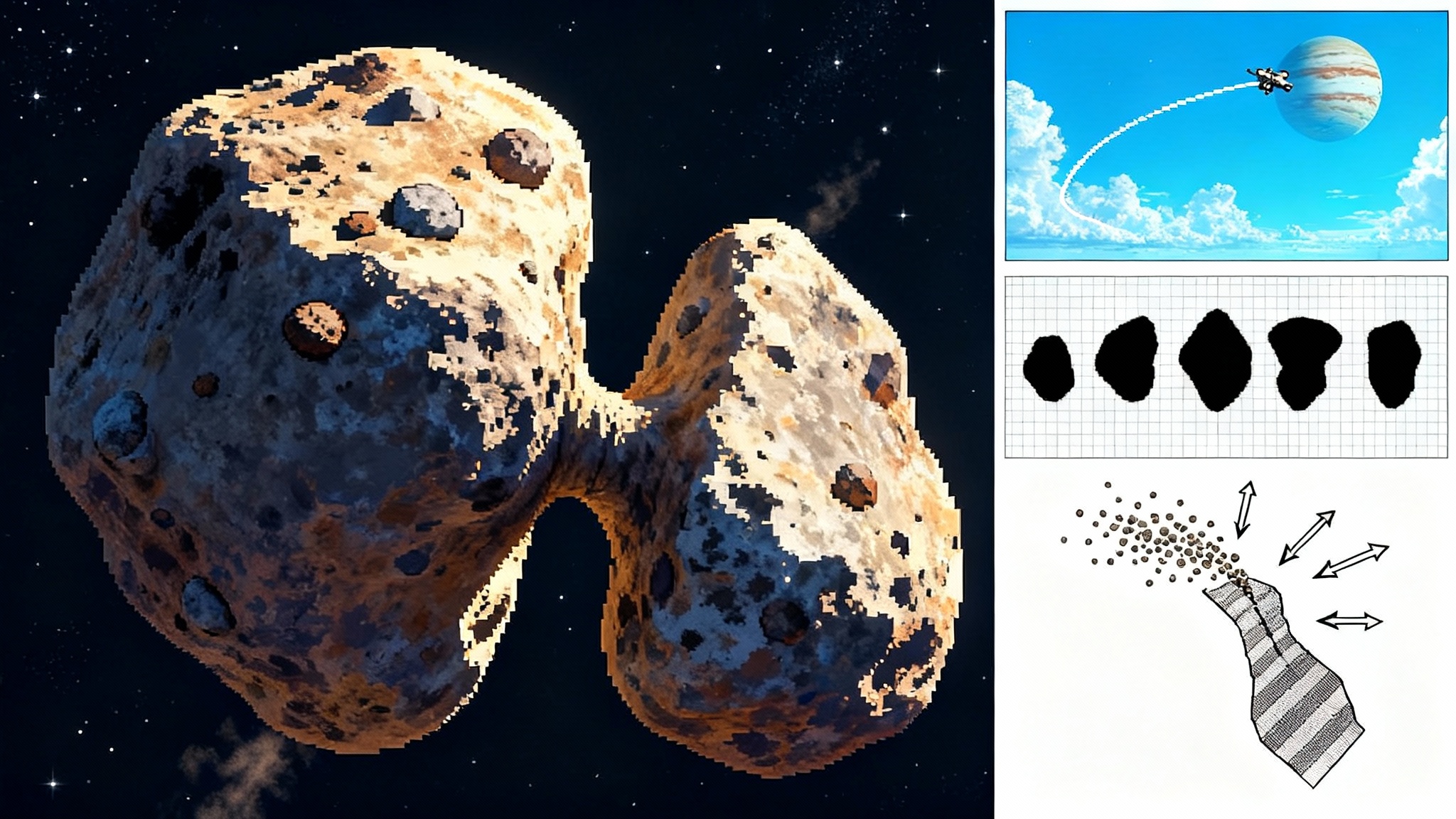
Lucy’s bowling-pin asteroid and the Trojan decade ahead
On April 20, 2025, NASA’s Lucy skimmed within 600 miles of asteroid Donaldjohanson and found a young bowling-pin contact binary. Here is what that geometry says about early solar system smashups, and the near‑term moves that can supercharge the Trojan encounters.
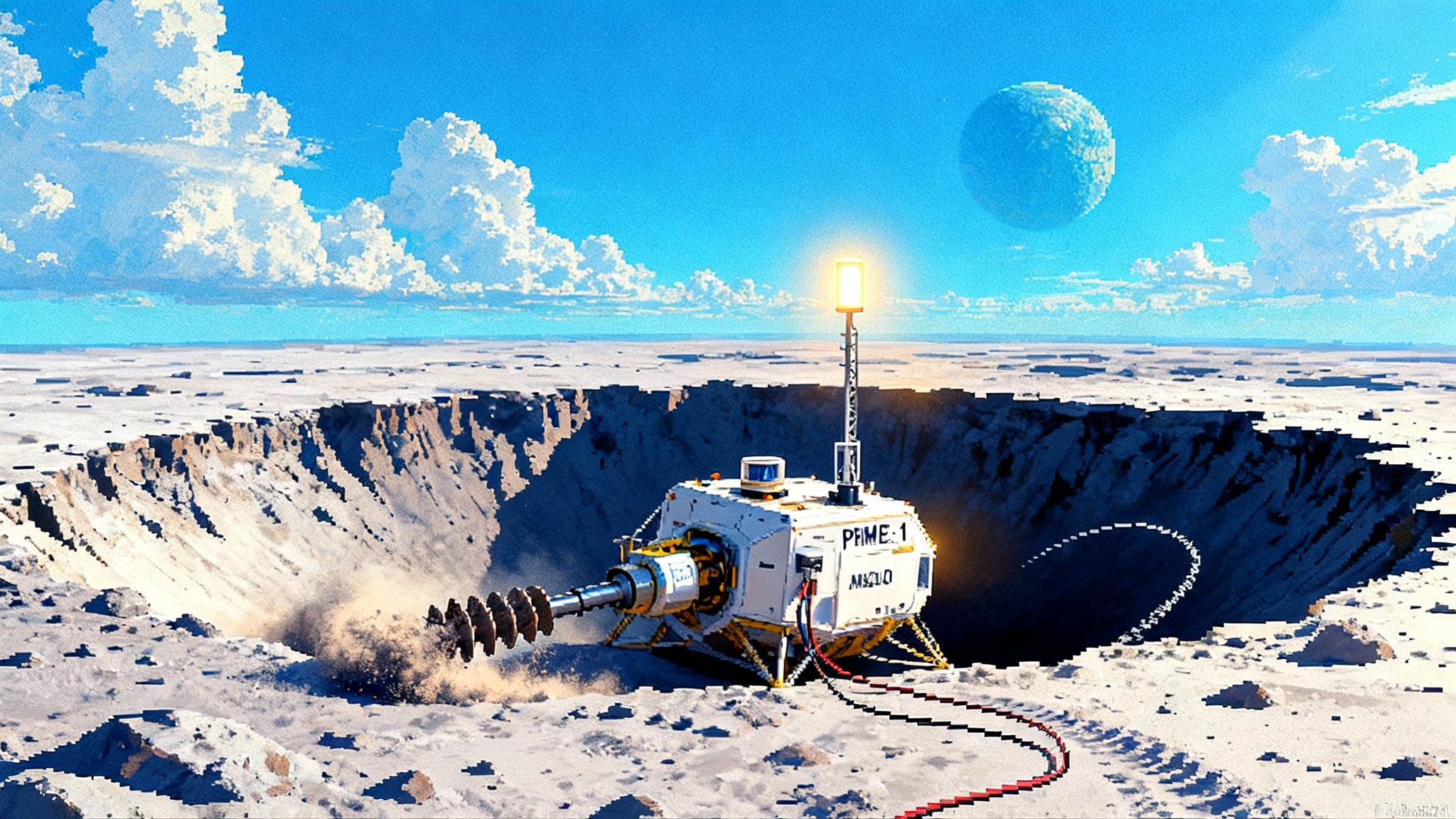
IM‑2’s tipped landing proved lunar prospecting is here
In March 2025, Intuitive Machines’ IM-2 lander reached the Moon’s south pole, tipped over in a crater, and still ran NASA’s TRIDENT drill and MSolo tests. That messy success marks the start of practical lunar resource prospecting and a fast CLPS learning curve.
MoM‑z14 rewrites cosmic dawn as JWST’s farthest galaxy
In May 2025, JWST confirmed MoM-z14 at redshift 14.44, a compact galaxy shining just 280 million years after the Big Bang. Its size, chemistry, and spectrum point to clustered starbursts, not a hidden black hole; and they force a rapid rewrite of how first light ignited. Here is what gets tested next and how ALMA, Euclid, and Roman can prove it.
Flight 11 and Block 3: The Turn to Operational Reuse
Starship Flight 11 closes the Block 2 era and points to a practical Block 3. Catching the booster, hardening the heat shield, and proving propellant transfer could compress costs and make monthly cislunar runs routine.
K2-18b’s biosignature showdown and the road to 5 sigma
Between April and September 2025, teams using JWST reported a 3 sigma hint of dimethyl sulfide or dimethyl disulfide in K2-18b’s atmosphere. Here is what that actually means and the fastest plan to confirm or refute it.
China’s Tianwen-2 targets a quasi-moon, then a comet
Launched May 29, 2025, China's Tianwen-2 will chase quasi-moon Kamoʻoalewa for a 2026 rendezvous, attempt anchor-and-attach sampling for a 2027 return, then slingshot to active asteroid 311P/PANSTARRS. Here is what to watch and why it matters.
New Glenn to Mars: ESCAPADE and the private interplanetary dawn
Blue Origin’s second New Glenn flight is set to send NASA’s twin ESCAPADE probes toward Mars. Pairing low cost smallsats with a commercial heavy lifter could reshape planetary science, enable real time Mars space weather maps, and set a faster deep space tempo through 2030.
Chang’e‑6 rewrites the Moon playbook: a cooler far side
Fresh peer-reviewed results from late September and early October 2025 show the lunar far side’s mantle is cooler, drier, and poorer in heat-producing elements than the near side. Here is what that means for site selection, power, ISRU, and radio science over the next five years.
A Starless Planet Caught in a Record Feeding Frenzy
A free-floating, Jupiter-mass world just set the fastest known accretion rate, blurring the line between planets and brown dwarfs and pointing to a fast path for finding many more starless worlds.
Makemake’s methane signals a new Kuiper Belt playbook
A faint methane glow above dwarf planet Makemake changes how we explore the Kuiper Belt. Here is a practical two-track plan, from a real-time Kuiper Belt Watch to a lean flyby that rides a Jupiter assist.
Uranus just gained a moon. Time to launch the orbiter
A fresh Uranus moon from JWST and crisp April 2025 occultations reshape ring hazards and entry conditions. Here is a concrete two-year plan to de-risk and fast-track a Uranus Orbiter and Probe.
NASA’s two-track bet to bring Mars samples home
NASA has funded two rival paths to land a Mars Ascent Vehicle and bring Perseverance’s samples home. Lock the right interfaces in 2025, hold the 2026 downselect, and Earth could see Mars rocks in the mid‑2030s. Slip again, and China may claim first return.
VIPER Reboot: Blue Origin to land NASA’s rover in 2027
NASA has brought VIPER back by tasking Blue Origin to prepare a 2027 south pole delivery. The option depends on Blue Moon MK1 completing its first landing later in 2025, a pivotal test for lunar logistics.
3I/ATLAS at Mars: The Interstellar Sprint We Must Catch
On October 3, 2025, the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS makes a rare pass by Mars. Here is what telescopes are racing to learn now—and the four concrete steps space agencies should lock in before the next one appears.
Enceladus’ fresh organics demand a 2030s life-hunt mission
A new Nature Astronomy result reports complex organics in freshly ejected Enceladus plume ice, strengthening the case for a fast-tracked orbiter-lander. Here is a pragmatic plan to pivot funding and schedules now and make a definitive life search fly in the 2030s.
Swift's rescue: NASA taps Katalyst for 2026 servicing
NASA has hired Katalyst Space Technologies to rendezvous with the Swift Observatory and push it to a safer orbit in 2026, a first-of-its-kind commercial capture that could reset how agencies extend satellite lifetimes in low Earth orbit.
Starship Flight 11 Closes V2, Opens the Road to V3
Targeted for mid October 2025, SpaceX’s Flight 11 will trial a five engine landing burn and harsher heat shield conditions. Here is what those choices signal about rapid reuse, near term cislunar logistics, and how a clean run could pull 2026 to 2027 milestones forward.